To create transistors engineers layered doped germanium to make two layers back to back in a configuration of either P-N-P or N-P-N. When the voltage at the base is greater than 06V or whatever your transistors V th might be the transistor starts saturating and looks like a short circuit between collector and emitter.
 Pnp Transistor How Does It Work Symbol Working Principle Electrical4u
Pnp Transistor How Does It Work Symbol Working Principle Electrical4u
The emitter E base B and collector C.

Transistor theory for dummies. To get an idea of how a transistor works specifically a FET think of a pipe connecting a source of water to a drain with a controllable valve across a section of the pipe as shown here. A transistor also acts as a switch to choose between available options. By controlling whether the valve is fully closed fully open or partially open you control the flow of water from the source to the drain.
Introduction So far in EE100 you have seen analog circuits. Typical base widths are about 10-6 m. E V S V B 0 V.
Then you learned how circuit elements do not operate the same at all frequencies. You started with simple resistive circuits then dynamical systems circuits with capacitors and inductors and then op-amps. Much more research was involved to complete the theory for filing a patent for the junction transistor filed June 25 th 1948.
Junction Transistors BJTs There are two types of BJTs the npn and pnp The two junctions are termed the base-emitter junction and the base-collector junction In order for the transistor to operate properly the two junctions must have the correct dc bias voltages the base-emitter BE junction is forward biased. Contents vii Other bipolar transistor types 138 Darlington pair circuit 139 Field-effect transistors 139 FET handling problems 143. 2 Transistor Basics The base is lightly doped and sandwiched between the collector and the emitter.
Diodes and Transistors 1. The base region is much thinner than the either the collector or emitter regions. In a standard NPN transistor you need to apply a voltage of about 07V between the base and the emitter to get the current flowing from base to emitter.
A transistor is an electronic component used in a circuit to control a large amount of current or voltage with a small amount of voltage or current. The principle of operation of the two transistor types PNP and NPN is exactly the same the only difference being in their biasing and the polarity of the power supply for each type. HttpsgooglFa8FYLIf you would like to support me to keep Simply Electronics going you.
William Shockley one of the inventors of the transistor once explained transistor-amplifiers to a student in a more humorous way. The current flowing in the base circuit affects the current flowing between the collector and the emitter. Uses of a transistor.
A functional n-p-n junction transistor was demonstrated on April 20 th 1950 enabled by the work of Gordon Teal and Morgan Sparks. When V GS. Active Region - the transistor operates as an amplifier and Ic βIb 2.
The point of contact was called a junction thus the name junction transistor. This means that it can be used to amplify or switch rectify electrical signals or power allowing it to be used in a wide array of electronic devices. I though Id do a video explaining the difference between NPN and PNP why they exists and how we can use them.
A very small current on. The collector region is usually thicker than the emitter as the largest. For any value of V DS.
Bipolar transistors have the ability to operate within three different regions. Lets take a look at the basics of transistors. A transistor acts as an Amplifier where the signal strength has to be increased.
When the voltage at the base is less than 06V the transistor is in cutoff mode -- no current flows because it looks like an open circuit between C and E. The transistor works because of something called a semiconducting material. The collector is moderately doped and the emitter is heavily doped.
The way that a 2N2222 BC107 BC108 and BC109 transistor symbol maps to the physical device is shown in the diagram below. Transistors 122 Bias for linear amplifiers 128 Transistor parameters and linear amplifier gain 132 Transistor packaging 136 Noise 137 Voltage gain 137. The transistor amplifies current - bipolar transistors are current devices unlike thermionic valves vacuum tubes and FETs which are voltage devices.
The bipolar transistor has three terminals named the emitter base and collector. A current flowing from the base to the emitter opens the flow of current from the collector to the emitter. MOS Transistor Qualitative Description Assume an n-channel receives its name from the type of channel present when current is flowing device with its source and substrate grounded i.
Transistors A transistor can be used as a switch and signal amplifier. Transistors with different part numbers wont necessarily have the pins in the same order. If you take a bale of hay and tie it to the tail of a mule and then strike a match and set the bale of hay on fire and if you then compare the energy expended shortly thereafter by the mule with the energy expended by yourself in the striking of the match you will understand the concept of amplification.
Transistors have three pins called emitter e baseb and collectorc. A Transistor is a three terminal semiconductor device that regulates current or voltage flow and acts as a switch or gate for signals. Full-fledged transistors were the next step.
It is an electronic device with three contacts.
The Lagrangian of QED is given by. Gauge theory class of quantum field theory a mathematical theory involving both quantum mechanics and Einsteins special theory of relativity that is commonly used to describe subatomic particles and their associated wave fields.
Mario A Serna Jr Geometry Of Gauge Theories
One can find in 34 an interesting discussion of the history of gauge symmetry and the discovery of YangMills theory 50 also known as non-abelian gauge theory At the classical level one replaces the gauge group U1 of electromagnetism by a compact gauge group G.
Gauge theory for dummies. Gauge symmetry is different from global symmetry in that the former is ambiguous while the latter is intrinsic in nature. This was a very successful theory that described the interactions of electrons positrons and photons. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators.
L 1 4F. One key element of the Standard Model of particle physics is that its a gauge theory which means certain types of symmetries are inherent in the theory. The material is based upon lecture notes for a course I teach from time to time at Utah State University on Classical Field Theory.
The following is version 13 of the text. In physics a gauge theory is a type of field theory in which the Lagrangian does not change under local transformations from certain Lie groups. In other words the dynamics of the system stay the same under certain types of transformations.
They are aimed at beginning graduate students. Modern theories describe physical forces in terms of fields eg the electromagnetic field the. A description of the same thing in different languages is called a Duality.
Gauge symmetry had been disregarded for a long time until the discovery of quantum mechanics in the twentieth century. When we describe things in physics we have always some freedom in our description. It is roughly the same as version.
Associated with any Lie group is the Lie algebra of group. The transformations between possible gauges called gauge transformations form a Lie groupreferred to as the symmetry group or the gauge group of the theory. We briefly sketch the history of gauge theories from Maxwell to Yang-Mills theory and the.
Where ψ ψx t is the wave function for the electron of rest mass m with spacetime coordinates x tThe p 1 p 2 p 3 are the components of the momentum understood to be the momentum operator in the Schrödinger equationAlso c is the speed of light and ħ is the. That state-of-the-art is described by a gauge field theory hence the dumbed-down title of these lectures called the Standard Model of particle physics of which the Higgs boson recently discovered at the CERN LHC is a key part. A gauge theory is a type of theory in physicsThe word gauge means a measurement a thickness an in-between distance as in railroad tracks or a resulting number of units per certain parameter a number of loops in an inch of fabric or a number of lead balls in a pound of ammunition.
This is historically the rst and also the simplest example of a gauge theory. The first and simplest known gauge theory is quantum electrodynamics QED. The simplest gauge theory Electromagnetism Let us now study some of the salient eld theoretic properties of electromagnetic theory.
The idea of a gauge theory evolved from the work of Hermann Weyl. A gauge symmetry is analogous to how we can describe something within one language through different words synonyms. Gauge theories refers to a quite general class of quantum field theories used for the description of elementary particles and their interactions.
Methods of classical relativistic eld theory. We shall see that certain structural features familiar from KG theory appear also for electromagnetic theory and. The Dirac equation in the form originally proposed by Dirac is.
The economic analogy in the article below is an excellent guide to the meaning of gauge symmetry as long as you have some electromagnetism knowledge. These lecture notes provide an introduction to the basic physics of non-Abelian gauge theories in four dimensions and other strongly coupled field theories in lower dimensions. The lecture notes are long around 400 pages but bite-sized chunks can be downloaded below.
A force that operates through a gauge field is transmitted with a gauge boson. Scalar elds spinor elds gauge elds and gravitational elds are treated. The term gauge refers to any specific mathematical formalism to regulate redundant degrees of freedom in the Lagrangian.
For example it doesnt matter what coordinate system we choose. Maxwell theory may be regarded as a prototype of gauge theory and generalized to nonabelian gauge theory.
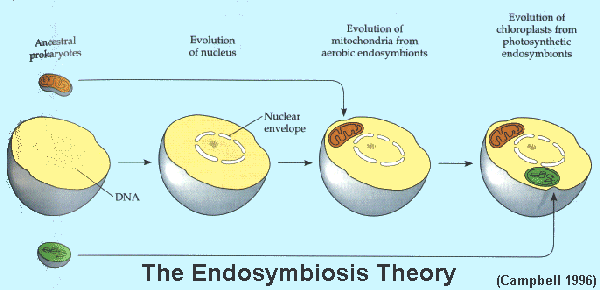
Eukaryotic cells are believed to have evolved from early prokaryotes that were engulfed by phagocytosis. Even though the individual single-celled organisms remained separate and could survive.
 The Endosymbiosis Theory Evolution Of Cells Earth Science Class Video Study Com
The Endosymbiosis Theory Evolution Of Cells Earth Science Class Video Study Com
The first step of the evolution of a eukaryotic cell is the infolding of the cellular membrane.
Explain the theory of endosymbiosis. Endosymbiotic theory designates a class of hypotheses that view various organelles in eukaryotic cells as descendants of endosymbionts whereby the term endosymbiont designates a microbial cell that has come to live stably inside another microbial cell a host. The hypothesised process by which prokaryotes gave rise to the first eukaryotic cells is known as endosymbiosis. Developed by Lynn Margulis.
Endosymbiosis is the theory that eukaryotic cells were formed when a prokaryotic cell ingested some aerobic bacteria. The chloroplastsof red algae green algae and plants evolved from an endosymbiotic cyanobacteriumliving within a mitochondria-containing eukaryotic host cell. An overview of the endosymbiosis theory of eukaryote origin symbiogenesis.
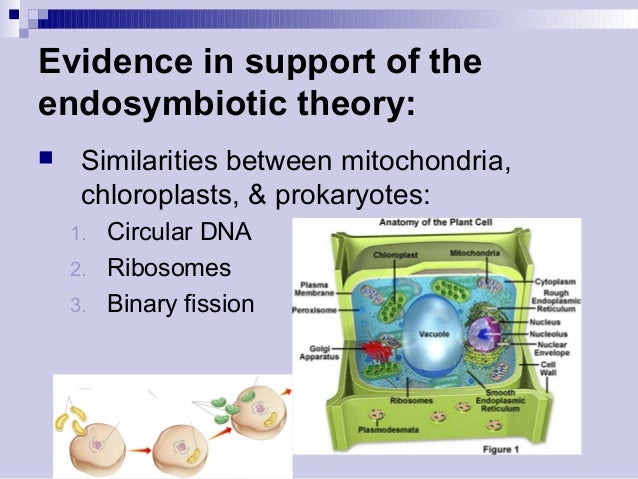
Ii Size of Ribosomes. The theory proposes that these organelles evolved from certain types of bacteria that eukaryotic cells engulfed through phagocytosis. Whats more the evidence for endosymbiosis applies not only to mitochondria but to other cellular organelles as well.
This theory suggests that mitochondria and plastids in eukaryotic cells were once. All eukaryotic cells like your own are creatures that are made up of the parts of other creatures. I Presence of DNA.
The theory of how mitochondria chloroplasts and other membrane-bound organelles in eukaryotic cell likely arose from a symbiosis between aerobic prokaryotes and host anaerobic eukaryotic ancestors. The theory holds that mitochondria plastids such as chloroplasts and possibly other organelles of eukaryotic cells are descended from formerly free-living prokaryotes taken one inside the other in endosymbiosis. The endosymbiotic theory states that some of the organelles in eukaryotic cells were once prokaryotic microbes.
An endosymbiont is one organism that lives inside of another one. Endosymbiotic theory proposes that these organelles were once prokaryotic cells living inside larger host cells. The prokaryotes may initially have been parasites or even an intended meal for the larger cell somehow escaping digestion.
The theory that explains how this could have happened is called endosymbiotic theory. Symbiogenesis explains the origins of eukaryotes whose cells contain two major kinds of organelle. Mitochondria and chloroplasts are the same size as prokaryotic cells and divide by binary fission.
Endosymbiotic theory Also known as the theory of serial endosymbiosis SET was postulated by the American evolutionary biologist Lynn Margulis in 1967 to explain the origin of eukaryotic cells. Based on decades of accumulated evidence the scientific community supports Marguliss ideas. Endosymbiosis is the best explanation for the evolution of the eukaryotic cell.
Mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own ribosomes which have 30S and 50S subunits not 40S and 60S. 10 Evidence of endosymbiotic theory. Iii Inhibition by.
Endosymbiosis is the process in which one organism lives within the other and the endosymbiont is the organism that lives within the other organism. Endosymbiosis Now that we know about both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells lets look at the endosymbiosis theory. Mitochondria the important energy generators of our cells evolved from free-living cells.
How Eukaryotic Cells Evolve Endosymbiotic Theory History. This process takes place when the plasma membrane folds inwards and develops an envelope around a smaller prokaryotic cell. Endosymbiosis also explains the origin of mitochondria and chloroplast.
So in accordance with the endosymbiotic theory every eukaryotic cell that we see today is actually composed of a number of other cells which were once whole in themselves. Symbiogenesis or endosymbiotic theory is the leading evolutionary theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic organisms. Ribosome exists either in a larger form the 80s typical of the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells.
The idea that chloroplasts were originally independent organisms that merged into a symbiotic relationship with other one-celled organisms dates to t. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. First proposed by Boston University biologist Lynn Margulis in the late 1960s the.
Mitochondria and Chloroplast DNA exists in closed circular form as it does in a prokaryotic cell. The theory of how mitochondria chloroplasts and other membrane-bound organelles in eukaryotic cell likely arose from a symbiosis between aerobic prokaryotes. Mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA which is circular not linear.
In her theory of endosymbiosis Lynn Margulis emphasizes that during the history of life symbiosis has played a role not just once or twice but over and over again. The endosymbiosis theory postulates that The mitochondriaof eukaryotesevolved from an aerobic bacterium probably related to the rickettsias living within an archaeal host cell.
Updated January 09 2020 The endosymbiotic theory is the accepted mechanism for how eukaryotic cells evolved from prokaryotic cells. For this discussion describe the theory of endosymbiosis in your own words and identify and discuss one line the evidence for this.
 How Did Endosymbiosis Happen Socratic
How Did Endosymbiosis Happen Socratic
Endosymbiotic theory Also known as the theory of serial endosymbiosis SET was postulated by the American evolutionary biologist Lynn Margulis in 1967 to explain the origin of eukaryotic cells.
The theory of endosymbiosis. All eukaryotic cells like your own are creatures that are made up of the parts of other creatures. Schimper a botanist born in France in 1856 made the observation that the chloroplasts that are found in photosynthetic organisms had many similar characteristics to cyanobacteria. The theory holds that mitochondria plastids such as chloroplasts and possibly other organelles of eukaryotic cells are descended from formerly free-living prokaryotes taken one inside the other in endosymbiosis.
For this discussion describe the theory of endosymbiosis in your own words and identify. Endosymbiosis--the symbiotic relationship where one symbiotic organism living inside another. Endosymbiosis is the best explanation for the evolution of the eukaryotic cell.
The mitochondria and chloroplast are thought to have once been free-living prokaryotes that were engulfed by an early eukaryote and incorporated into the functioning of that cell. In her theory of endosymbiosis Lynn Margulis emphasizes that during the history of life symbiosis has played a role not just once or twice but over and over again. The Theory of Endosymbiosis.
A representation of the endosymbiotic theory An endosymbiont or endobiont is any organism that lives within the body or cells of another organism most often though not always in a mutualistic relationship. The chloroplastsof red algae green algae and plants evolved from an endosymbiotic cyanobacteriumliving within a mitochondria-containing eukaryotic host cell. An endosymbiont is one organism that lives inside of another one.
The theory that explains how this could have happened is called endosymbiotic theory. Mitochondria the important energy generators of our cells evolved from free-living cells. The endosymbiotic theory states that some of the organelles in todays eukaryotic cells were once prokaryotic microbes.
She proposed it as the explanation for how complex cells evolved. The framework for the idea of endosymbiosis began with work done by Andreas Schimper in 1883. Symbiogenesis or endosymbiotic theory is the leading evolutionary theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic organisms.
The Theory of Endosymbiosis. The mitochondria and chloroplast are thought to have once been free-living prokaryotes that were engulfed by an early eukaryote and incorporated into the functioning of that cell. The idea that chloroplasts were originally independent organisms that merged into a symbiotic relationship with other one-celled organisms dates to t.
An endosymbiont is a cell which lives inside another cell with mutual benefit Eukaryotic cells are believed to have evolved from early prokaryotes that were engulfed by phagocytosis The engulfed prokaryotic cell remained undigested as it contributed new functionality to the engulfing cell eg. In this theory the first eukaryotic cell was probably an amoeba-like cell that got nutrients by phagocytosis and contained a nucleus that formed when a piece of the cytoplasmic membrane pinched off around the chromosomes. Whats more the evidence for endosymbiosis applies not only to mitochondria but to other cellular organelles as well.
The term endosymbiosis is from the Greek. It involves a cooperative relationship between two cells which allow both to surviveand eventually led to the development of all life on Earth. Where did this theory come from.
The endosymbiotic theory states that some of the organelles in prokaryotic cells were once from eukaryotic organisms. Post author By a b.
Endosymbiotic theory proposes that these organelles were once prokaryotic cells living inside larger host cells. Based on decades of accumulated evidence the scientific community supports Marguliss ideas. Instead of the traditional tree of life branching out from a few common ancestors to many descendent species Margulis proposes that branches have separated and then come.
Post date February 15 2021. The hypothesized process by which prokaryotes gave rise to the first eukaryotic cells is known as endosymbiosis and certainly ranks among the most important evolutionary events. Biologist Lynn Margulis proposed the idea of endosymbiosis about 50 years ago.
The endosymbiosis theory postulates that The mitochondriaof eukaryotesevolved from an aerobic bacterium probably related to the rickettsias living within an archaeal host cell. The prokaryotes may initially have been parasites or even an intended meal for the larger cell somehow escaping digestion.
Meet the holographic principle. Part 1 of 3 - https.
 Testing The Holographic Universe Neurologica Blog
Testing The Holographic Universe Neurologica Blog
In our current timeline we refer to the matrix grids virtual reality simulation and hologram.

Holographic universe theory for dummies. The holographic principle says gravity comes from thin vibrating strings which are all holograms of a flat 2D Universe. Up down left right forward back past future. Or so our primitive Ple.
The Holographic Universe The theory that reality as we consciously experience it is not real goes back to ancient indigenous people who believed we exist in a dream or illusion. Recent advances in telescopes and sensing equipment have allowed scientists. Size3size4fontComic Sans Ms THE HOLOGRAM UNIVERSECUM REALITYA SIMPLIFIED VIEW Go to radio shows-listen to Michael Talbots talk on The Holographic Universe-be a VIP Member The whole way we viewperceive REALITY itself has been thrown into a conundrum.
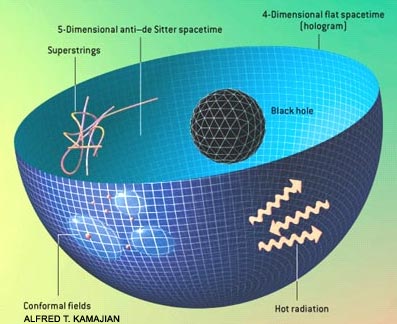
Recently Raphael Bousso while at Stanford University helped formulate a more. In other words the holographic principle says that everything that happens in a space can be explained in terms of information thats somehow stored on the surface of that space. First proposed by Gerard t Hooft.
It raises an interesting hypothesis about the true state of reality but it is mere speculation. As pointed out by Raphael. The idea is called the holographic principle after the way that a hologram encodes 3D information on a 2D surface.
The idea that our universe isnt entirely real is a theory that dates back to beginnings of human civilization. When viewing a hologram you can tilt the image and see the orientation of the shape move. The AdS stands for anti-de Sitter a particular solution of Einsteins general relativity that describes a completely empty universe with a negative spatial curvature.
Its as if you see the object in the picture from a different angle. Some scientists think the universe is a hologram and it could lead to a unified theory of everything. Our thought processes are much more intimately connected to the physical world than has been previously thought.
Many societies held a belief at some level that human existence occurs in a state that is one of illusion or is based on a dream. Its a pretty boring. The holographic principle suggests that.
Essentially it claims our. First proposed by Gerard t Hooft it was given a precise string-theory interpretation by Leonard Susskind who combined his ideas with previous ones of t Hooft and Charles Thorn. The holographic universe theory is just an observational theory.
The holographic universe principle suggests that were living in a simulated reality this is different from the hypothesis that states we live in a computer simulation. For example picture a 3-dimensional space that resides inside the 2-dimensional curled surface of a cylinder as in this figure. The Holographic Theory of The Universe Explained Explained.
And it was done by the Scientific. A holographic model for the universe explains lucid dreams in which such dreams are visits to parallel realities. As well as this it is important to note that the philosophy we have explored here is part of the wider doctrines of each philosopher.
Well as you said the holographic principle is the idea that the universe around us which we are used to thinking of as being three dimensional we have three dimensions of space is actually at a more fundamental level two dimensional and that everything we see thats going on around us in three dimensions is actually happening in a two-dimensional space. Theres a web post from the Nature website going around entitled Simulations back up theory that Universe is a hologram Its an interesting concept but suffice it to say the universe is not a. Synchronicity can be explained by the holographic model.
The Holographic Universe-for dummies - posted in General Discussion. The holographic principle is a tenet of string theories and a supposed property of quantum gravity that states that the description of a volume of space can be thought of as encoded on a lower-dimensional boundary to the regionsuch as a light-like boundary like a gravitational horizon. We live in a universe with 3 dimensions of space and one of time.
Holographic Universe The holographic principle is a property of quantum gravity theories which resolves the black hole information paradox within string theory. A hologram is a 2-dimensional image that contains all the 3-dimensional information of an object. One of the most cutting-edge theories in theoretical physics the holographic principle holds that the universe is 3D image projected off a 2D surface much like a hologram emerges from a sheet of.
A hologram is a flat two-dimensional surface that when viewed appears to have a third dimension in other words it gives the illusion of having depth. We may experience time in a linear fashion but it is a virtual reality experience. The process of making a hologram is called holography.