During the ionic bonding metals electrons are lost for positive ion formation and the non-metals. The nearer the difference in electronegativity between atoms comes to zero the purer the covalent bond becomes and the less polarity it has.
 8 4 Bond Polarity And Electronegativity Chemistry Libretexts
8 4 Bond Polarity And Electronegativity Chemistry Libretexts
The ability of an atom in a molecule to attract shared electrons is called electronegativity.

How does electronegativity affect bonding. As a rule an electronegativity difference of 2 or more on the Pauling scale between atoms leads to the formation of an ionic bond. When it is large the bond is polar covalent or ionic. This effect only holds true for a row in the periodic table because the attraction between charges falls off rapidly with distance.
As you move from left to right. When two atoms combine the difference between their electronegativities is an indication of the type of bond that will form. The ability of an atom in a molecule to attract shared electrons is called electronegativity.
The electronegativity depends upon the nature of the electronic configuration. The more electronegative an atom is the more its bonds to other atoms will have ionic character especially to elements that have metallic character. The electronegativity of the central atom does not really influence bond angles in any meaningful way.
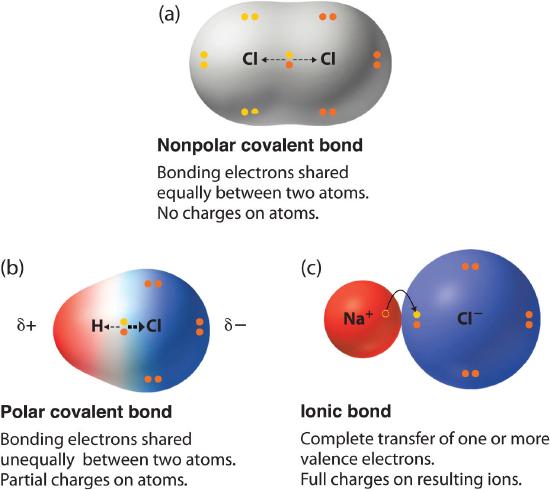
When a chlorine atom covalently bonds to another chlorine atom the shared electron pair is shared equally. A small electronegativity difference leads to a polar covalent bond. A difference of less than 2 between atoms leads to covalent bond formation.
An atoms electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus. Across a period from left to right the electronegativity of atoms increases. If the difference between the electronegativities of the two atoms is small neither atom can take the shared electrons completely away from the other atom and the bond will be covalent.
In part b Ca has a low electronegativity. The electronegativity affects the chemical bond in the following. The electron density that comprises the covalent bond is located halfway between the two atoms.
A large electronegativity difference leads to an ionic bond. Electronegativity is a measure of an atoms attraction for the electrons in a bond. Therefore electronegativity increases from left to right in a row in the periodic table.
The higher the electronegativity of an atom the greater its attraction for bonding electrons. The most strongly electronegative atom is fluorine. The chart shows electronegativities from sodium to chlorine ignoring argon since it does not does not form bonds.
When two atoms combine the difference between their electronegativities is an indication of the type of bond that will form. Polar bonds and polar molecules. Since O is more electronegative than S CaO is more polar and therefore is more readily dissolved in water.
In a simple molecule like HCl if the bond is polar so also is the whole molecule. The compound with the greatest difference in electronegativity between the atoms in the compound is the most polar and therefore most soluble compound. No electronegativity difference between two atoms leads to a pure non-polar covalent bond.
The results also show that electronegativity is a major influence on covalent bond lengths and the set of electronegativity scale and covalent radii proposed in this work can be used to calculate covalent bond lengths in different environments that have not yet been experimentally measured. Ionic bonding being a chemical bond gives rise to ions that are opposite charged in nature. When a fluorine atom bonds to almost any other atom except another F atom the bond has ionic character because of partial transfer of an electron from the other atom to fluorine.
The size of atoms and the orbitals used and useable are much more important. Electronegativity is a measure of the attraction of an atom for the electrons in a chemical bond. The most electronegative atom is fluorine F.
Electronegativity and Bond Type The absolute value of the difference in electronegativity ΔEN of two bonded atoms provides a rough measure of the polarity to be expected in the bond and thus the bond type. In VSEPR theory electronegativity of atomsgroups will effect bond angles due to changes in the distribution of electron pairs around the central atom and thus changes in severity of electron pair repulsion. Electronegativity is the strength an atom has to attract a bonding pair of electrons to itself.
When the difference is very small or zero the bond is covalent and nonpolar. Electronegativity symbol χ measures the tendency of an atom to attract a shared pair of electrons or electron density.