A product with a PES of more than 1 is said to be elastic. The formula for calculating the co-efficient of elasticity of demand is.
Now work out the numerator of the formula which represents the percentage change in quantity.
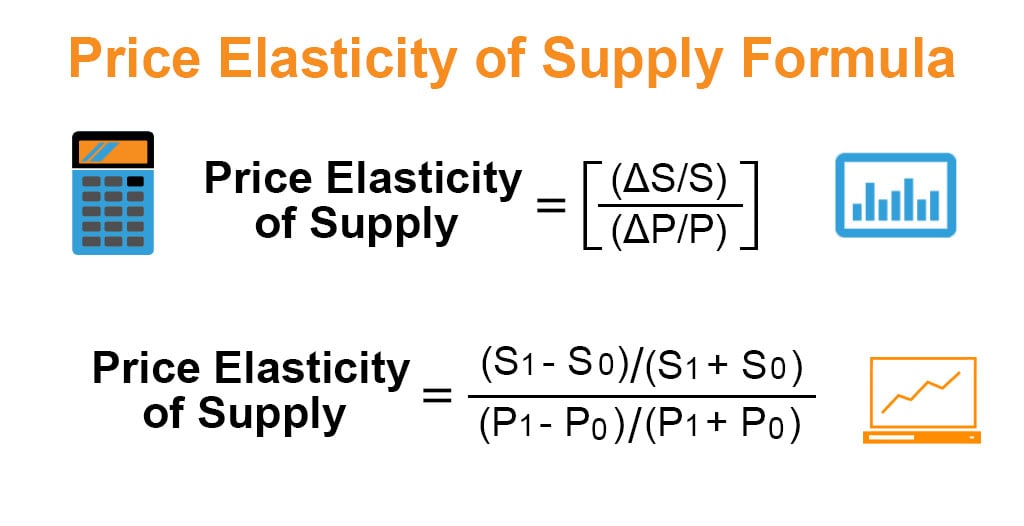
How to calculate price elasticity. Price Elasticity of Demand Change in the Quantity Demanded ΔQ Change in the Price ΔP Price Elasticity of Supply Change in the Quantity Supplied ΔQ Change in the Price ΔP Examples of Price Elasticity Formula With Excel Template. Calculate the price elasticity of supply using the mid-point formula when the price changes from 5 to 6 and the quantity supplied changes from 20 units per supplier per week to 30 units per supplier per week. Start by dividing the expression on top of the equation.
Work out the expression on the top of the formula. Percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price Since changes in price and quantity usually move in opposite directions usually we do not bother to put in the minus sign. Price Elasticity of Demand can be determined in the following four steps.
Price elasticity is the concept showing where the demand responds to price change with certain elasticity. If price rises from 50 to 70. We divide 2050 04 40.
The price elasticity of demand studies the inverse trend for the elasticity of normal goods. Finally input the final quantity of your product. Lets take an example to explain it.
So in this example the price elasticity of supply when the price increase from 10 to 12 is 0625 625. Identify P 0 and Q 0 which are the initial price and quantity respectively and then decide on the target. Percent change in quantity Q2 Q1 Q2 Q12 100 percent change in quantity Q 2 Q 1 Q 2 Q 1 2 100.
When price changes a little the supply of the product will change by a larger percentage. How is the price elasticity of demand measured. How to use the price elasticity of demand calculator.
You can then use the midpoint formula to find the price elasticity of demand. Change in Price To calculate a percentage we divide the change in quantity by initial quantity. Then input the initial quantity of your product.
So in order to calculate the price elasticity of demand following formula can be used. The next thing to input is the final price which is also a monetary value. To calculate elasticity we will use the average percentage change in both quantity and price.
This is called the midpoint method for elasticity and is represented by the following equations. Input the current price Input the new price Input the current quantity Input the new quantity Click on the Calculate button to generate the results. Lets look at the practical example mentioned earlier about cigarettes.
To calculate elasticity instead of using simple percentage changes in quantity and price economists use the average percent change. Price elasticity of supply PES measures how responsive supply of an item in relation to changes in its price. Tags elasticity example microeconomics price elasticity of demand.
A product with a PES of 1 is said to be unit elastic. Because 150 and 2000 are the initial price and quantity put 150 into P 0 and. To measure you the price elasticity of demand you would record the price at which you sold a product and how much of the product you sold at one time then change the price and measure how much of the product was sold again over the same period of time.
Calculating Elasticity The formula for calculating elasticity is. Price elasticity of demand change in QD. Example 2 - Using the Midpoint Formula.
The trick to solving point price elasticity of demand problems is to find the coefficient on the price P and then to plug the corresponding price and quantity values in to the point price elasticity of demand formula. First input the initial price which is a monetary value. Plug in the values for each symbol.
When you calculate the elasticity at two different points using the point elasticity you will likely result in different numbers. This is called the mid-point method for elasticity and is represented in the following equations. After having the percentage change in price and quantity supplied we simply plug these figures into the PES formula to calculate the supply elasticity of this product.
To calculate the price elasticity of demand heres what you do. Price Elasticity of Demand percent change in quantity percent change in price Price Elasticity of Demand percent change in quantity percent change in price. After that you can simplify using algebra.
To generate the values you need follow these simple steps. Say because a products price decreases from 10 to 8 the quantity demanded increases from 40 units to 60 units.
Demonstration on how to determine equ. The formula that you use to calculate equilibrium price and quantity is QdQs and then following the steps that are outlined above.
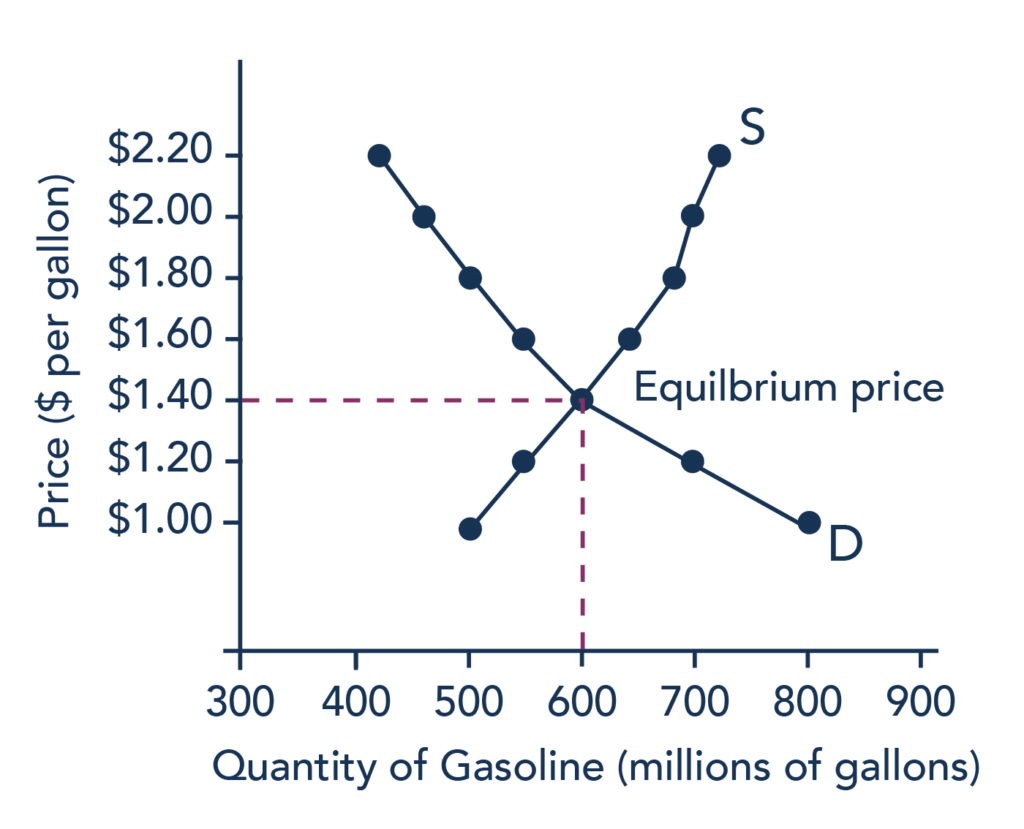 Equilibrium Price And Quantity Introduction To Business
Equilibrium Price And Quantity Introduction To Business
This is done by simply.

How to determine equilibrium price. In its most basic form a linear supply function looks as follows. At equilibrium level of output OX price is equal to its marginal cost and marginal cost curve cuts the MR curve from below. The firm enjoys normal profits.
200 150 x Price 500 - 50 x Price. 300 20 20P 20 P 15. Divide both sides of the equation by 200.
How to Calculate Equilibrium Price and Quantity 1 Calculate Supply Function. Evidently at the equilibrium price both buyers and sellers are in a state of no change. In other words find the price when the quantities Q s and Q d are the same.
This is the equilibrium price. How to determine the price mathematically. When a product experiences a change in supply rather than a change in demand level the supply formula is the formula that needs to be switched to determine the products new equilibrium price.
Set quantity demanded equal to quantity supplied. In economics the equilibrium price represents the price that if practiced on the market will result in the fact that the whole quantity that is supplied is presumably sold meaning that on the market the economic forces named generally as the supply and demand are balanced and that there are no external influences that may have an impact on the price mechanism. Now suppose demand increases from DD to D 1 D 1 and the industry is in equilibrium at point E 1 which determines the price OP 1 The new price OP 1 is less than the new market price ie OH.
Add 100 to both sides of the equation. Suppose the Supply function is Qs 40P and the demand function is Qd 1000 60P. 200 Price 300.
Similar to the supply function we can calculate the demand function with the help of a. Equilibrium Price and Quantity Calculator The Calculator helps calculating the Equilibrium Price and Quantity given Supply and Demand curves In microeconomics supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. Hence there will be one equilibrium price at which the demand by the buyers is equal to the supply by the producers.
Set quantity demanded equal to quantity supplied. Under monopoly for the equilibrium and price determination there are two different conditions which are. By substituting P and Q values to both demand and supply equations equilibrium price and quantity can be found as follows.
While it is helpful to see this graphically its also important to be able to solve mathematically for the equilibrium price P and the equilibrium quantity Q when given specific supply and demand curves. Add 50P to both sides of the equation. If the equilibrium is now disturbed and the price rises to OP 1 the quantity of the good supplied is OQ 2 will exceed the quantity demanded OQ 1.
Marginal revenue must be equal to marginal cost. Equilibrium Price Equilibrium means a state of no change. Explanation of examples and diagrams.
Technically at this price the quantity demanded by the buyers is equal to the quantity supplied by the sellers. Find the equilibrium price. To find the equilibrium price you want to find the price at which the two equations intersect.
Just like before solve. You get P equals 200 per box. At this point the quantity supplied and the quantity demanded is equalat the equilibrium price the market is said to clear.
The equilibrium price and quantity in a market are located at the intersection of the market supply curve and the market demand curve. Add 50P to both sides of the equation. To determine the equilibrium price do the following.
QS mP b. Qs 200 150 x Price. How to Find Equilibrium Price.
2 Calculate Demand Function. 300-10p 0 10P. If for instance your given the supply function and the demand function and we know that an equilibrium price is only reached when quantity supplied is equal to quantity demanded we can easily solve for the equilibrium price.
Tutorial on how to solve for quantity demanded and quantity supplied using equations algebra used in economics class. Let us suppose we have two simple supply and demand equations Qd 20 - 2P Qs -10 2P. The equilibrium price is established at the point where the two curves intersect.
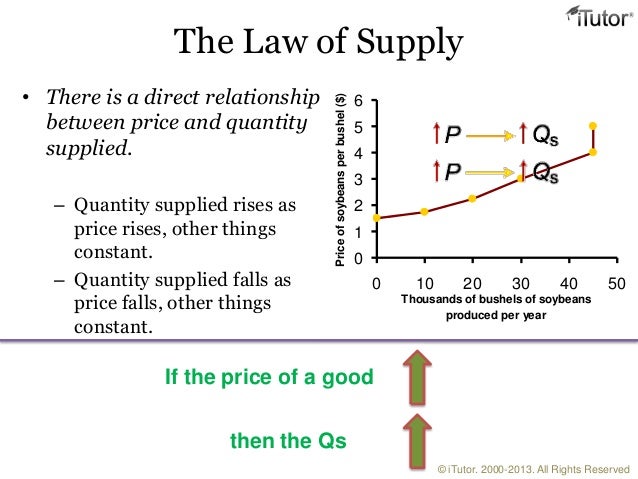
A shows the relationship between price and quantity supplied. Relationship between price and the quantity demanded We know thatthe demand curve shows the relationship between the price andquantity demandedin a given market.
As the price goes up quantity supplied increases.
The relationship between price and quantity supplied is. The quantity of ice cream cones supplied each month by Ben an ice-cream seller at various prices of ice cream. In other words there is a direct relationship between price and quantity. B indicates the quantity demanded at each price in a series of prices.
Negative There is a _________ relationship between price and quantity demanded according to the law of demand. Marketing and Sales Questions Answers for AIEEEBank ExamsCAT AnalystBank ClerkBank PO. Relationship between Price and Quantity Supplied.
A supply curve relates to a graph that is used in economics to show. Other things equal when price of a good rises the quantity supplied of the good also rises and when the price falls the quantity supplied falls as well. The larger the number of buyers in a market the lower will be product price C.
The law of supply states that when all other factors are held constant an. The supply curve is a graphical presentation of the relationship between price and quantity supplied. A direct inverse B inverse direct C inverse inverse D direct direct and A decrease in quantity demanded as distinct from a decrease in demand is depicted by a.
The supply curve is a graphic representation of the correlation between the cost of a good or service and the quantity supplied for a given period. This relationship between price and quantity supplied is called the law of supply. Price and quantity demanded are inversely related B.
There exists a direct or positive relationship between price and quantity supplied. It indicates direct relationship between the two variables Price and quantity supplied. The law of supply is a fundamental principle of economic theory which states that keeping other factors constant an increase in price results in an increase in quantity supplied.
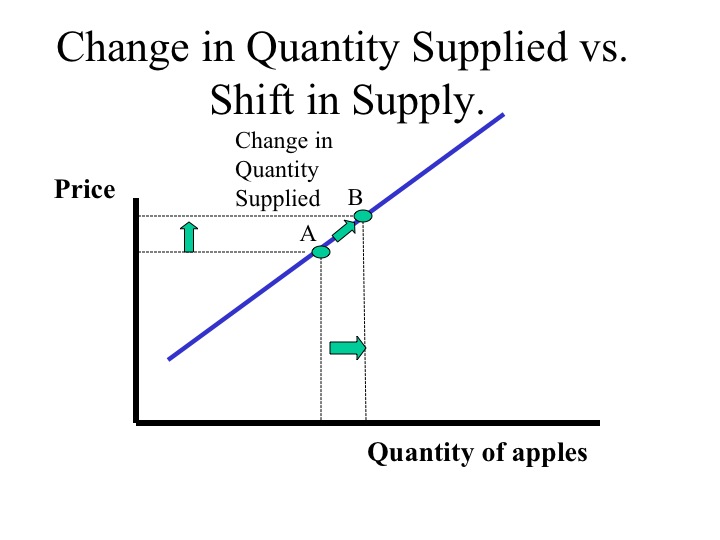
Price changes cause changes in quantity supplied represented by movements along the supply curve. A move from point x to point y. The relationship between quantity supplied and price is _____ and the relationship between quantity demanded and price is _____.
D shows the relationship between income and spending. The law of demand states that. The supply curve is upward sloping.
We also know that the view the full answer. Price and quantity supplied are directly related. As price goes down the quantity supplied decreases.
When Price increases to Rs5 he expands supply to 50 units. Quantities respond in the same direction as price changes. There is a _____ relationship between price and quantity supplied according to the law of supply.
The relationship between quantity supplied and price is ____ and the relationship between quantity demanded and price is _____. The schedule shows that with an increase in price the quantity supplied is also increasing. When this price- quantity relationship is plotted on a graph we get a supply curve that slopes upwards.
The price elasticity of supply measures the responsiveness of a change in price and the corresponding change in quantity supplyThe elasticity of supply is a positive coefficientThis is because positive relationship between price and the quantity suppliedThe determinant is Time Frame for the. The relationship between quantity supplied and price is. This relationship between price and quantity supplied is called the law of supply.
Other things equal when the price of a good rises the quantity supplied of the good also rises and when the price falls the quantity supplied falls as well. C graphs as an upsloping line. A supply curve is a graphical illustration of the relationship between price and B.
At a price below 100 Ben does not supply any ice cream at all. In a typical illustration the price will appear. Therefore the relationship between the price and quantity supplied is direct.
Firms prefer to supply more products to the markets at higher prices because they will make more profits. The law of supply explains d the positive relationship between price and quantity supplied. The law of supply states that ceteris paribus as the price of a commodity rises falls its supply rises falls.
Price and quantity demanded are directly related. 1 the seller offers only 10 units for sale. When the price is Re.
At various prices of ice cream.