Determine the displacement of the spring - lets say 015 m. After knowing the spring constant we can easily find how much force is needed to deform the spring.
 Forces And Elasticity Examples Solutions Videos Notes
Forces And Elasticity Examples Solutions Videos Notes
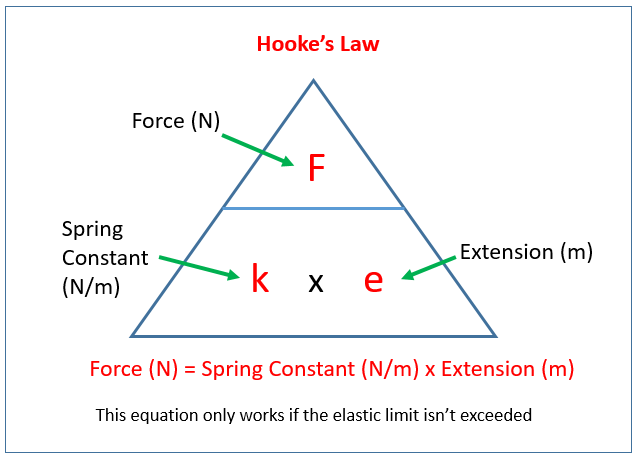
K is the spring constant.

Calculate the spring constant. Looking only at the magnitudes and therefore omitting the negative sign you get. It is a proportionality constant that describes the relationship between the strain deformation in the spring and the force that causes it. Before we get into my awesome experiment Ill go over my model.
The equation can be shaped for the value of k. So the question tells you that F 6 N and x 03 m meaning you can calculate the spring constant as follows. The unloaded length of a spring is measured.
Force F is measured in newtons N spring constant k is measured in newtons per metre Nm. How to Calculate the Spring Constant Model Derivation. K 20 Nm.
First the formula for hookes law must be manipulated to solve for k the spring constantTo do this we simply divide. How to Calculate Spring Constant. How to use the Hookes law calculator Choose a value of spring constant - for example 80 Nm.
Next we must measure. There are two main ways to calculate spring rate. Our elastic potential energy calculator uses the following formula.
Spring constant can be defined as the force required per unit extension or unit compression of the spring. Materials with larger spring constants are stiffer. Force spring constant extension F ke This is when.
The spring constant of a spring can be found by carrying out an experiment. Equivalent Spring Constant Series When putting two springs in their equilibrium positions in series attached at the end to a block and then displacing it from that equilibrium each of the springs will experience corresponding displacements x 1 and x 2 for a total displacement of x 1 x 2We will be looking for an equation for the force on the block that looks like. 3 m 2 0 N m.
The spring constant is 20 Nm. Spring Constant K Now the Spring constant is defined as the force required per unit of extension of the spring. After reaching this point it was time to collect some data.
Nm m N. K frac text F text e k 3 N 015 m. 03 m6 N.
Hookes Law is a principle of physics that states that the that the force needed to extend or compress a spring by some distance is proportional to that distance. In equation form Hookes Law is Fkx where F is the force needed x is the distance the spring is stretched or compressed beyond its natural length and k is a constant of proportionality called. The other is by practical measurement.
F -kΔx -80 015 12 N. How to calculate a spring constant. Spring constant can be calculated using Hookes Law equation.
I should note that the project actually. Spring potential energy equation. K F x.
E 15 cm 015 m. K F x 6 N 0. If we hang a mass from a spring and measure its stretch how can we determine the spring constantHW K 10 14.
Substitute them into the formula. You can also use the Hookes law calculator in. Hookes law is a law of physics that states that the force F needed to extend or compress a spring by some distance x scales linearly with respect to that distancethat is F s kx where k is a constant factor characteristic of the spring ie its stiffness and x is small compared to the total possible deformation of the spring.
Calculate spring force constant k based on the Hookes Law based on the force 50 N distance from equilibrium of 30 mm and spring equilibrium position of 20 mm. Record each stretching force in N. F -k x -- k -Fx What are the units of k in Hookes Law.
Next we must measure our first variableIn this case we will first measure the force acting on the spring. U ½kΔx 2. Slotted masses are added to the spring.
Begin aligned ktext N 03text m text Nm end aligned k. F kx Now we need to rework the equation so that we are calculating for the missing metric which is the spring constant or k. The law is named after 17th-century British physicist.
Some people like the form. One is through calculations based upon looking at and measuring the spring. The practical measurement is the most accurate form when carried out with the correct equipment.
In order to figure out how to calculate the spring constant we must remember what Hookes law says.
X is the displacement of the spring from its equilibrium position. We can also visualise this spring-mass motion with the help of uniform circular motion.
 Hooke S Law Calculate The Force From A Spring When Given Its Spring Constant And Deflection Calculate A Spring Constant Given The Required Force And Ppt Download
Hooke S Law Calculate The Force From A Spring When Given Its Spring Constant And Deflection Calculate A Spring Constant Given The Required Force And Ppt Download
Hookes law equation states that F kx where F is the force required to compress.

Units for spring constant. So before we try to define spring constant and understand the workings of spring constant we need to look at Hookes law. For continuous media each element of the stress tensor σ is a force divided by an area. If you think about what this means in terms of units or inspect the Hookes law formula you can see that the spring constant has units of force over distance so in SI units newtonsmeter.
Therefore the spring constant k and each element of the tensor κ is measured in newtons per meter Nm or kilograms per second squared kgs 2. K is the spring constant Nm x is the displacement m positive for displacement negative for compression Spring Constant Definition. Unit of spring constant is Nm.
The higher the spring constant the harder it is to compress or stretch it. K is the spring constant in Nm-1. Letter K is spring constant and it has the units as Nm.
Spring constant definition is related to simple harmonic motions and Hookes law. This value is also a measure of elasticity. Newtons per millimeter per 360º degrees or.
What is the spring constant in this situation. Spring Constant Dimensional Formula. 1000N -k3m 1000N3m -k.
Show activity on this post. The unit of the spring constant k is the newton per meter Nm. According to Newtons Third Law of Motion when spring is pulled it pulls back with a restoring force.
Substituting the units into your formula you get. To find the units of spring constant you can use the hooks law which says F k x where F force unit Newton k spring constant x expansion or contraction unit m So by this equation you can get that k F X So you get the units as Nm. The larger the spring constant the stiffer the.
A spring constant is a measure of a springs ability to resist compression and elongation. It is analogous to the spring constant of a linear spring. What is the si unit of spring constant.
Is a constant with units of newton-meters radian variously called the springs torsion coefficient torsion elastic modulus rate or just spring constant equal to the change in torque required to twist the spring through an angle of 1 radian. Lets say that a force of 1000N extends a spring at rest by 3 meters. Learn more about Hookes law and how to calculate the spring constant including the formula insight on a springs impact on force and an example problem.
Physics 24032020 2210 sandhu2840. The spring constant k is a measure of the stiffness of the spring. The units for the spring constant k are Newtons per meter Nm.
The spring constant can be determined by simple algebraic analysis. For example torsion spring which works due to turning of the spring. This restoring force follows the Hookes Law which relates the force of the spring to the spring constant.
To calculate the required torsion spring constant you must divide the torque in inch-pounds or newton-millimeters by the degrees of deflection thus leaving you with a torsion spring rate result measured in inch-pounds per degree or newton-millimeters per degree. The spring constant shows how much force is needed to compress or extend a spring or a piece of elastic material by a given distance. This answer is not useful.
Force by the action of the spring is given by F -kx k is known as the spring constant or stiffness constant. Belen Armstrong 13 April 0940. K is the spring constant x is the deformation or displacement of the spring from its initial position m m So the units for a spring constant are Nm Nm Become a member and unlock all.
The units are both N m 1 or kg s 2. If a force F is considered that stretches the spring so that it displaces the equilibrium position by x. We can ignore the 4 π 2 since it is a dimensionless unitless constant.
The units of measurement for the constant amount of force per unit of travel a compression or extension spring is able to exert is measured in pounds of force per inch lbfin or newtons per millimeter Nmm. It is different for different springs and materials. Kg s 2 kg s 2.
There are different types of spring. According to the theory of elasticity when a load is applied o a spring it will naturally extend proportionally as. Force of the spring - spring constant k times displacement.
The units of the mass m is kg and the units of the period T is s. For torsion springs the spring constant torque units are inch-pounds of torque per 360º degrees or inch-pounds of torque per degree. In other words the spring constant is the force applied if the displacement in the spring is unity.
It is therefore measured in units of pressure namely pascals Pa or Nm 2 or kgms 2.