These nucleic acids are involved in three basic processes in our body like replication transcription and translation. This information is stored in multiple sets of three nucleotides known as codons.
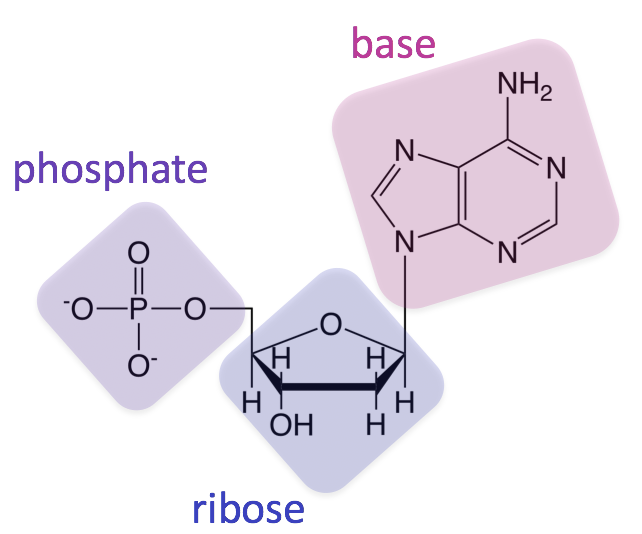
Each nucleotide in turn is composed of three distinct elements.
What does nucleic acid do. Humans--and all other living organisms--need nucleic acids. There are five types of nitrogenous bases in nucleic acids. They carry the genetic blueprint of a cell and carry instructions for the functioning of the cell.
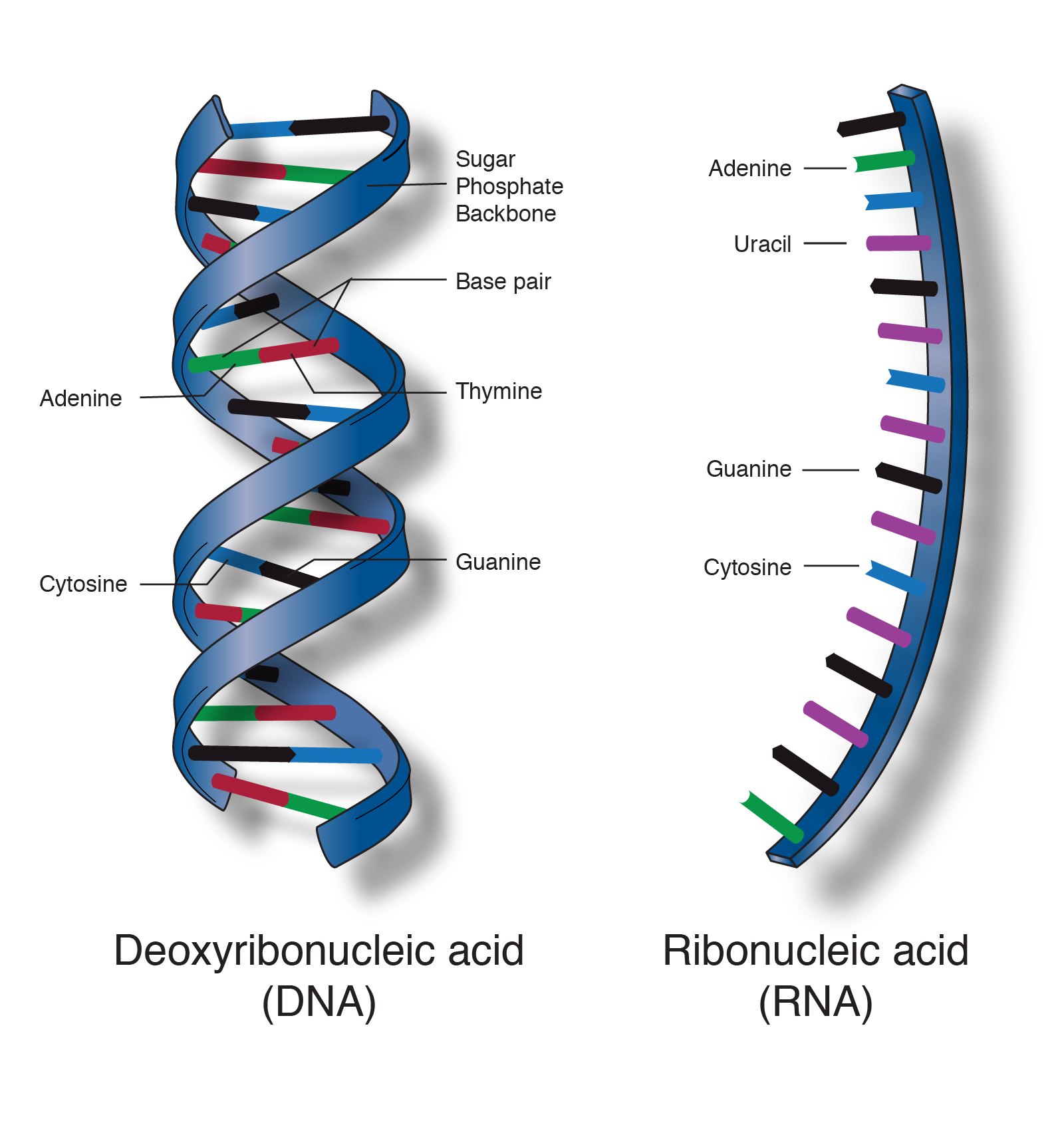
Nucleic acid is an important class of macromolecules found in all cells and viruses. Nucleic acids are naturally occurring chemical compounds that serve as the primary information-carrying molecules in cells. In deoxyribonucleic acid DNA hydrogen bonds form between specific bases of two nucleic acid chains forming a twisted double-stranded DNA molecule that looks like a spiral staircase with the two sugar-phosphate chains as side rails and the base pairs forming the rungs.
The functions of nucleic acids have to do with the storage and expression of genetic information. Nucleic acids consist of a series of linked nucleotides. This is the currently selected item.
Nucleic acids are formed when nucleotides come together through phosphodiester linkages between the 5 and 3 carbon atoms. Nucleic acids are also ingested from food like herring mackerel etc. Interestingly they also found to be presentin space as per NASA.
Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA encodes the information the cell needs to make proteins. And experimentally added nucleic acids are capable of activating both innate and adaptive immune systems and inducing a sterile inflammatory response. The nucleic acids are vital biopolymers found in all living things where they function to encode transfer and express genes.
Nucleic acids are macromolecules that store genetic information and enable protein production. Nucleic acids include DNA and RNA. A five-carbon ribose sugar a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base.
Out in the cytoplasm or liquid medium of the cell the mRNA serves as a working template of genetic information for the protein-producing machinery. Nucleic acid naturally occurring chemical compound that is capable of being broken down to yield phosphoric acid sugars and a mixture of organic bases purines and pyrimidines. There is extensive literature that suggests that extraneously added nucleic acids have biological actions.
They copy information from the DNA and then leave the nucleus. Biology is brought to you with support from the Amgen Foundation. A nucleic acid is a chain of nucleotides which stores genetic information in biological systems.
Although the COVID-19 situation is gradually abating in China nucleic acid tests are becoming a larger part of peoples daily lives as the country has been conducting widspread testing to ensure. These are vital molecules present in all the living cells on the earth. A nucleic acid sequence is the order of nucleotides within a DNA GACT or RNA GACU molecule that is determined by a series of letters.
Nucleic acids called mRNA for messenger ribonucleic acid form in the nucleus. What Do Nucleic Acids Do. Humans--and all other living organisms--need nucleic acids.
These nucleic acids are digested and metabolized in the digestive tract small intestine by a series of enzymes which are present in the pancreatic juice and intestinal juices. Nucleic acids are the main information-carrying molecules of the cell and by directing the process of protein synthesis they determine the inherited characteristics of every living thing. DNA and RNA structure.
These molecules are composed of long strands of nucleotides. The nucleic acids which include deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA and ribonucleic acid or RNA encode genetic information and allow humans and other organisms to follow their genetic instructions. Adenine A cytosine C guanine G thymine T and uracil U.
The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid DNA and ribonucleic acid RNA. If you have children your genetic information will be recombined and united. They play an especially important role in directing protein synthesis.
These large molecules are called nucleic acids because they were first identified inside the nucleus of cells however they are also found in mitochondria and chloroplasts as well as bacteria and viruses. It creates DNA and RNA which store the information needed by cells to create proteins. Sequences are presented from the 5 to 3 end and determine the covalent structure of the entire molecule.
They can enter into cells in vitro and in vivo and induce genetic transformation and cellular and chromosomal damage. Nucleic acids are the most important macromolecules for the continuity of life. Nucleic acids are the components of our nuclear material Chromosomes present in the cells.
The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid DNA and ribonucleic acid RNA. Nucleotides are composed of a nitrogenous base a five-carbon sugar and a phosphate group. Molecular structure of RNA.
DNA and RNA are considered as nucleic acids. Nucleic acids store and transmit genetic information that you inherited from your parents.