If you want to know about the accounting process just read the following steps in the accounting cycle. Steps in the Accounting Cycle 1 Transactions.
 Accounting Cycle Steps Double Entry Bookkeeping
Accounting Cycle Steps Double Entry Bookkeeping
Post journal entries to applicable T-accounts or ledger accounts.
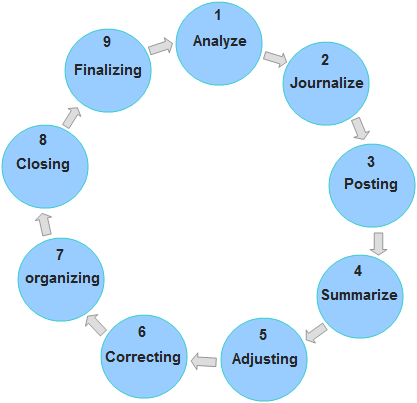
What are the steps in accounting cycle. It covers everything from analyzing measuring and recording transactions to adjusting balances and closing the books. The accounting cycle is a nine-step process businesses use to compile all of the information needed to prepare important financial statements. Closing books of accounts at the end of an accounting period and.
Preparing an unadjusted trial balance is the next step of the accounting cycle in which a total balance is calculated for all the individual accounts. The steps of Accounting Cycle lists the process of analyzing monitoring and identifying the financial transactions of a company. Worksheets Evaluating a worksheet and identifying adjusting entries is the fifth step of the process.
Accounting cycle refers to the complete process of accounting procedure followed in recording classifying and summarizing the business transactions. Identifying and Analyzing Business Transactions. Its called a cycle because the accounting workflow is circular.
These include analyzing sales purchases and other business transactions and then recording those transactions in the monetary term into the key important areas like journal entries ledger accounts trial balance and then. Entering transactions manipulating the transactions through the accounting cycle closing the books at the end of the accounting period and then starting the entire cycle again for the next accounting period. The entitys financial statements are produced through analyzing and recordings the business transactions in many different steps of the accounting cycle.
Starting the cycle again for the next accounting period. Steps of Accounting Cycle The steps of accounting cycle include the processes of identifying collecting analyzing documents recording transactions classifying summarizing posting and preparing trial balance making journal entries closing the books and final reporting financial information of an organization. Thus Accounting Cycle includes.
Identify business events analyze these transactions and record them as journal entries. Processing classifying and adjusting the business transactions through the accounting cycle. Accounting cycle is the sequence of accounting procedures to record classify and summarize accounting information.
Accounting cycle is an accounting procedure starting from recording of business transactions and ends in final preparation of financial statements for reporting. The accounting cycle incorporates all the accounts journal entries T accounts T Accounts Guide If you want a career in accounting T Accounts may be your new best friend. A worksheet is prepared to ensure that debits and credits are equal to each other.
It is a step by step process of accounts collecting recording maintaining and reporting. Steps in accounting cycle. The income statement shows all the expenses incurred and incomes earned by the organization during a financial period.
The Accounting Cycle is a nine-step standardized practice used by organizations CPA firms to record and calculate financial transactions activities. Not all transactions and events are entered into the accounting system. Accounting cycle starts right from the identification of business transactions and ends with the preparation of financial statements and closing of books.
The key steps in the eight-step accounting cycle include recording journal entries posting to the general ledger calculating trial balances making adjusting entries and creating financial. It includes the initial transaction the preparation of financial documents and the closing of an account. Here we discuss the top 9 steps in the accounting cycle with diagram Collection of Data Journalizing Ledger Accounts Unadjusted Trial Balance Performing Adjusting Entries Adjusted Trial Balance Creating Financial Statements Closing the Books and Post-closing Trial Balance.
The next step in the accounting cycle is to organize the various accounts by preparing the financial statements namely income statement and balance sheet. Only those that pertain to the business entity are included in the process. The accounting process starts with finding the nature of transactions by analyzing the sources of account with respect to their effect on the financial position of the company.
1 Classify transactions 2 Journalizing them 3 Post to Ledger 4 Unadjusted Trial Balance 5 Adjusting Entries 6 Adjusted Trial Balance 7 Financial Statements 8 Closing Entries 9 Closing Trial Balance 10 Recording Reversing Entries. All the transactions are not entered into the accounting system. Accordingly an accounting cycle has the following nine basic steps.
Here are the 9 main steps in the traditional accounting cycle. The T Account is a visual representation of individual accounts debits and credits adjusting entries over a full cycle. A book keeper of company track all the process of accounting from the.
The accounting cycle is a series of steps used by an accounting department to perform maintenance of a companys financial transactions and oversee the recording process that follows. 10 Steps of Accounting Cycle are. Prepare an unadjusted trial balance from the general ledger.
The accounting process starts with identifying and analyzing business transactions and events.
You can calculate accounting cost by subtracting your expenses from your revenue. The result should be close to 1.
Indirect Cost Calculation And Process About Ala
Breakeven Formula Profit 0 sales variable costs fixed costs Target Net.
Formulas of cost accounting. Conversion Cost Direct material Factory overhead. The above mentioned is the concept that is elucidated in detail about Accounting Formulas for the Commerce students. Factory cost Direct material Direct labour Factory overhead.
An important part of standard cost accounting is a variance analysis which breaks down the variation between actual cost and standard costs into various components volume variation material cost variation labor cost variation etc so managers can understand why costs were different from what was planned and take appropriate action to correct the situation. When you subtract your fixed costs from contribution margin the amount left over is your profit. You multiply your sales per unit by units sold.
When you understand and use these foundational formulas youll be able to analyze a products price and increase profits. You can print it out and use it on the proctored. At the 1000-unit production level the total cost of the production is.
Financial accounting is primarily concerned with record keeping directed towards the preparation of Profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheet. The breakeven point is the level of sales where your profit is zero. To reduce and eliminate costs in a business you need to know the formulas that are most often used in cost accounting.
Subtract the cost of goods and services from net sales. If not the company is losing an. Materials price usage variance Actual quantity used Actual price Actual quantity used Standard price materials quantity usage variance formula.
Accounting 303 covers many aspects of cost accounting so this is a formula sheet with the information in one place for ratios and calculations. Economic costs represent any what-if scenarios. B Cost accounting is a science and arts both.
Cost accounting is a practice of cost control which is as follows-a Cost accounting is a branch of systematic knowledge that is a discipline by itself. Mathematically it is represented as Total Cost Total Fixed Cost Total Variable Cost. It consist its own principles concepts and conventions which may vary from industry to industry.
The breakeven formula is sales minus variable cost minus fixed cost. Beginning inventory value Purchases of inventory Ending inventory value Cost of goods sold. Cost pool total Cost driver The result will be a dollar amount that can then be multiplied by the number of products manufactured to obtain a total product cost for that cost pool.
It provides information regarding the. Materials purchase price variance Formula. 10 Average fixed cost 3 Average variable cost x 1000 Units 13000 Total cost.
Cost accounting formulas Net sales percentage. By the number of goods produced. Cost Accounting Formulas And Terminologies 1.
It is the source of all other functions of cost accounting as we can calculate the cost of sales per unit for a particular product. A calculation used in activity-based costing for determining the costs associated with activities based on particular time-based processes. Prime cost Direct material consumed Direct labour.
Divide net sales by gross sales. Example of the Total Cost Formula A company is incurring 10000 of fixed costs to produce 1000 units for an average fixed cost per unit of 10 and its variable cost per unit is 3. The formula for total cost can be derived by adding the total fixed cost to the total variable cost.
Materials purchase price variance Actual quantity purchased Actual price Actual quantity purchased Standard price Materials price usage variance formula. Sales Cost of goods sold Gross profit. The first function is to control the cost within the budgetary constraints management has set for a particular product or serviceIt is essential since management allocates limited resources to specific projects or production processes.
Prime Cost Direct Material Direct Labor2. The result as a percentage of net sales should be. Accounting costs represent anything your business has paid for.
The following formulas can be used to find out different costs. Beginning balance net income net losses dividends ending balance. Cost Accounting is a branch of accounting and has been developed due to limitations of financial accounting.
Financial Accounting Cost Accounting and Management Accounting 1 - 22 Study Note 2 Material Control 23-48 Study Note 3 Labor Cost Computation and Control 49-88 Study Note 4 Overheads 89-118 Study Note 5 Methods of Costing-Job Batch and Contract Costing 119-146 Study Note 6.